Resources for decision-making in diabetes
Published November 17, 2016
For World Diabetes Day (WDD), IHME showcased a variety of diabetes-related resources that can be used by decision-makers.
IHME’s WDD social media campaign demonstrated how IHME’s online data visualization tool GBD Compare can be used to compare trends across countries, ages, sexes, and time periods.
For example, here is a chart comparing rates of diabetes burden, measured in age-standardized disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) per 100,000, across different levels of development:
Years of healthy life lost due to #Diabetes increasing, globally: https://t.co/yskhzVpm9B #WDD @WorldDiabetesDay #WDD2016 pic.twitter.com/yUXriwfWsq
— IHME at UW (@IHME_UW) November 13, 2016
Using these metrics – age-standardization and DALYs – removes the effects of population and age differences across the two countries.
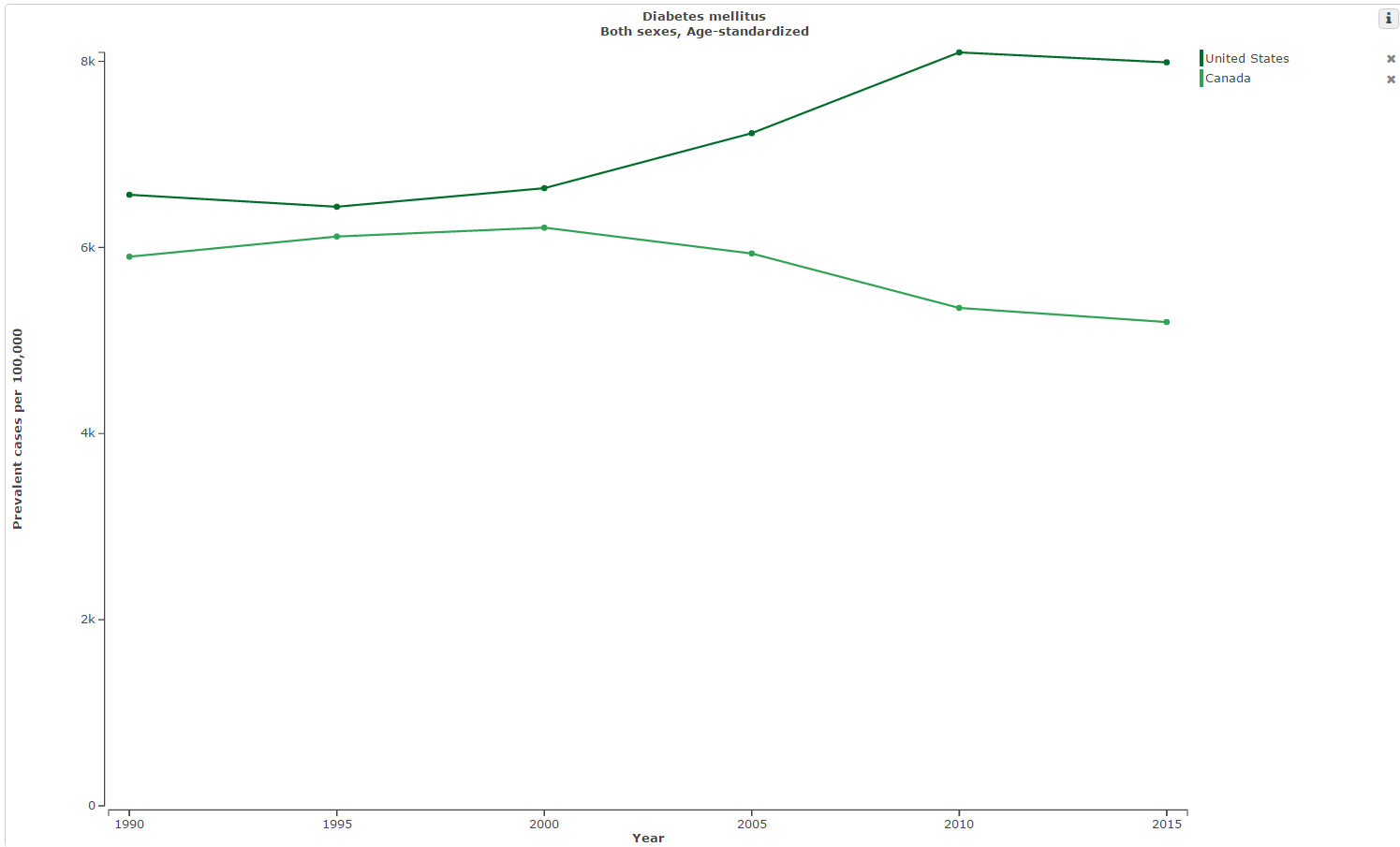
The GBD Compare tool also allows users to compare diabetes prevalence across countries. The example below shows age-standardized prevalent cases per 100,000 of diabetes in the US and Canada. To view this chart in the tool, visit http://ihmeuw.org/3yib.
Diabetes prevalence rates, US and Canada, 1990-2015
You can use the tool to see which countries rank highest for rates of disease burden from diabetes, and how that ranking has changed over time. Fiji and Trinidad and Tobago ranked first and second in 1990 and 2015, but Mauritius jumped from rank 26 in 1990 to rank three in 2015. Even though many countries’ rankings dropped between 1990 to 2015, rates of diabetes burden rose in every country featured in this chart during that period. For example, even though South Africa dropped from rank 16 in 1990 to rank 18 in 2015, diabetes burden rates increased by 54.4% in that country during this period.
#SouthAfrica has had a 54% increase in # of years of healthy life lost due to #Diabetes since 1990: https://t.co/s9drhgIQ7W pic.twitter.com/gBILFE88Nd
— IHME at UW (@IHME_UW) November 13, 2016
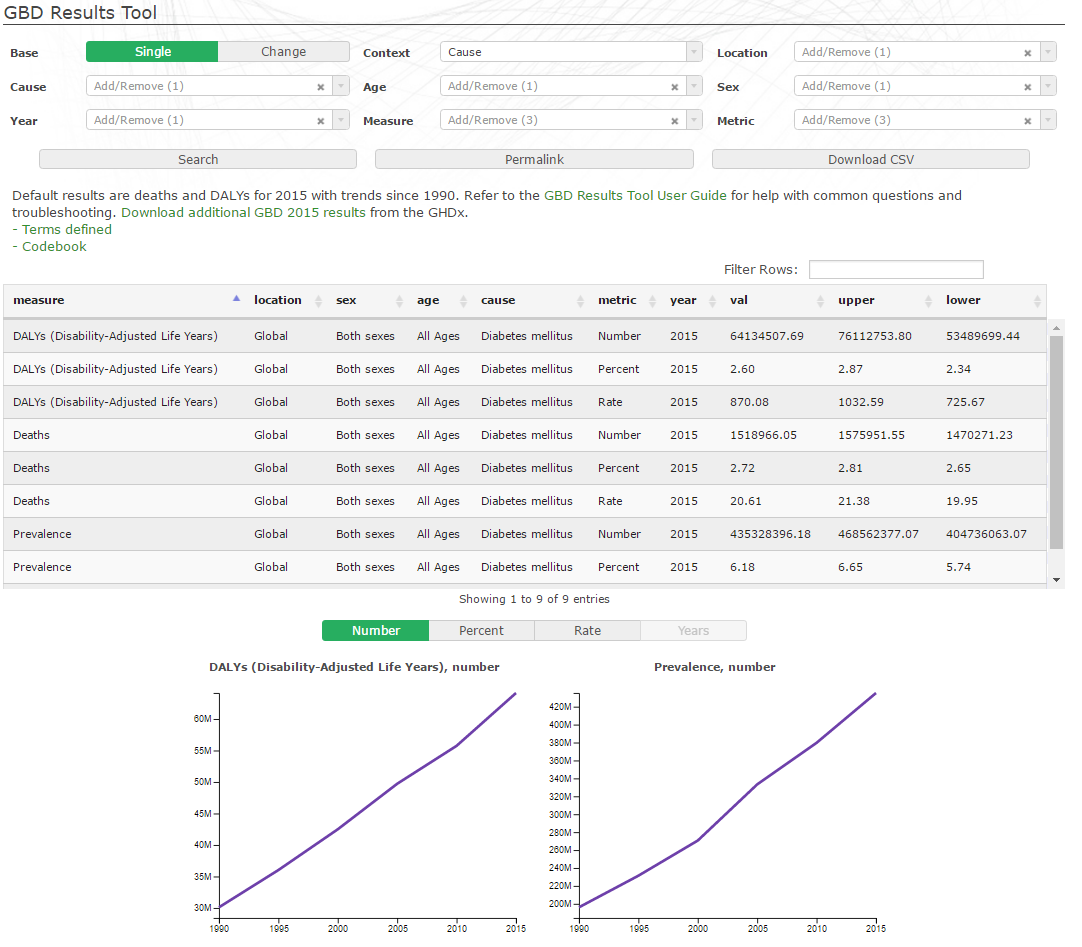
If you’re interested in downloading diabetes estimates from the Global Burden of Disease study, visit the GBD Results Tool.
IHME created an infographic entitled “Burden of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases in Africa, 1990-2015.” Rates of diabetes burden have been rising across Africa, and disproportionately affect women in many countries. For more information, read the associated news release.
Additionally, IHME has been researching diabetes prevalence and risk across communities in the US. In September 2016, IHME researchers published an article in Diabetes Care estimating diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes prevalence across counties from 1999 to 2012. The researchers found that diabetes prevalence ranged from 8.8% to 26.4% across counties, with the highest prevalence in Southern states with the exception of Florida, along the Texas-Mexico border, and in counties in the four corners region of the Southwest with Native American reservations.
Finally, IHME’s Twitter feed highlighted research published in PLOS One from the HealthRise project that looked at diabetes risk by zip code in three counties in Minnesota. The study’s authors ranked performance in four clinical indicators related to diabetes risk: reduction of high blood sugar (blood glucose – abbreviated as HbA1c in the graph), reduction of blood pressure, reduction of “bad” (low-density lipoprotein, or LDL) cholesterol, and smoking status. They found that zip codes with lower income, education, and insurance coverage tended to perform worse in these clinical performance metrics.
.@HealthRise ID's zip codes that have least effective control of #diabetes: https://t.co/mFklcogpOy #WDD16 #WDD @WorldDiabetesDay pic.twitter.com/2gebHoZiR7
— IHME at UW (@IHME_UW) November 14, 2016
Note: HbA1c: reduction of high blood sugar, smoking: non-smoking status, BP: reduction of blood pressure, LDL: reduction of “bad” (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol
To learn more about the GBD study, visit healthdata.org/gbd or read the report Rethinking Development and Health: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study.