Air pollution
Air pollution affects millions of people worldwide, stemming from diverse sources. Both household and outdoor air pollution pose severe threats related to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, cancers, and other conditions.
Photo by Sergei Karpukhin, Reuters.
What is the impact of air pollution on health?
Although death rates from air pollution overall have dropped by 29% from 1990 to 2019, deaths caused by ambient particulate matter rose 40% from 1990 to 2019, now constituting the 4th most deadly health risk worldwide. Different types of air pollution tend to stem from various causes:
- Outdoor air pollution consists of gases and tiny particles of solids or liquids that are suspended in the air, often called ambient particulate matter. This type of pollution comes from sources such as dust storms, forest fires, residential heating and cooking, agriculture, industry, and power production. Ambient particulate matter pollution is an important cause of premature death and illness worldwide.
- Household air pollution is also a major issue, mainly in rural areas of low-income countries. This results from burning solid fuels, such as wood, dung, and plant matter, while cooking indoors.
- Breathing polluted air has been linked to lower respiratory infections like pneumonia, cardiovascular disease – including ischemic heart disease and stroke – lung cancer, chronic respiratory diseases such as COPD, diabetes, and lower birthweight and premature births.
- Household air pollution and ambient particulate matter pollution are among the top risk factors for loss of healthy life years, according to the Global Burden of Disease study.
State of Global Air 2020
The State of Global Air report and interactive website bring into one place a comprehensive analysis of the levels and trends in air quality and health for every country in the world. They are produced annually by the Health Effects Institute and IHME's Global Burden of Disease (GBD) project and are a source of objective, high-quality, and comparable air quality data and information.

Key findings
The latest data from the Global Burden of Disease study reveals the extent and effects of air pollution on global health worldwide.
Air pollution is the 4th leading cause of death.
Air pollution is one of the top threats to global health, surpassed only by high blood pressure, tobacco use, and poor diet.

South Asia, Africa, and the Middle East are most affected by air pollution.
The South Asian nations of Bangladesh, India, Nepal, and Pakistan suffer over 1.5 million air pollution–related deaths annually. The highest average exposure rates for ambient fine particle air pollution were seen in South Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Globally, 95% of the world’s population – over 7 billion people – may live in areas with unhealthy air, as defined by the WHO threshold.
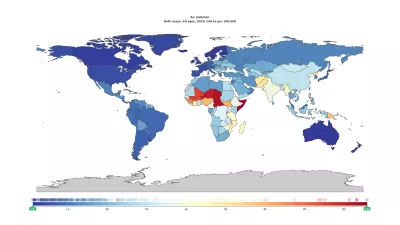
Household air pollution remains a serious threat to global health.
Around 49% of the world’s population, or about 3.8 billion people, are exposed to household air pollution from the burning of solid fuels for cooking (coal, crop waste, charcoal, wood, among others). This major cause of household air pollution is prevalent in low- and middle-income regions of Asia and Africa.