News releases
Read the latest news from IHME about published research.New IHME COVID-19 Projections: Mexico, Peru, and Ecuador Facing Combined Deaths of Nearly 20,000
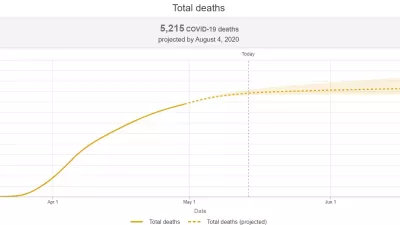
In its first forecasts for COVID-19 outside North America and Europe, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is preliminarily projecting nearly 20,000 deaths in Mexico, Peru, and Ecuador combined through early August.
People Begin Moving About as States Open Up, Leading IHME to Project Slight Increase in US COVID-19 Deaths
As some states continue to ease social distancing mandates and new data are acquired on people’s movements, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is projecting a slight increase in expected COVID-19 deaths in the US.
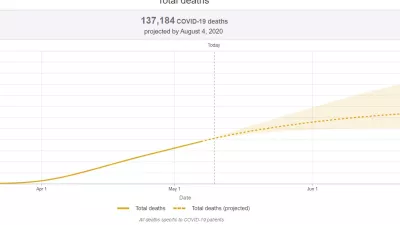
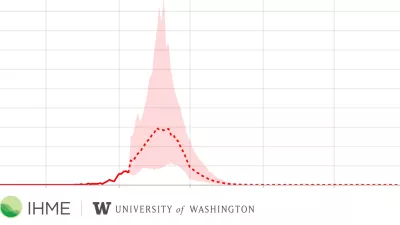
New IHME Forecast Projects Nearly 135,000 COVID-19 Deaths in US
New COVID-19 forecasts for the US project nearly 135,000 deaths through the beginning of August, according to the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington.
IHME to Hold Media Briefing at 4 PM (Eastern) Today (Details Below)
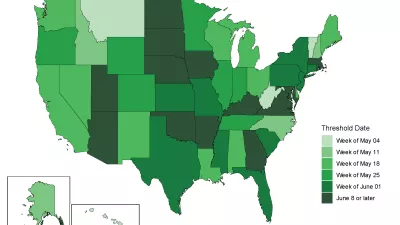
New COVID-19 state-by-state US analyses from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) find that as early as May 4, some states may be able to relax some aspects of social distancing measures so long as “robust containment strategies” are implemented to prevent a second wave of infections.
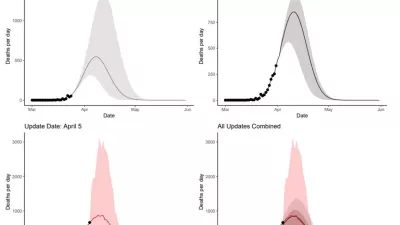
Correction in Uncertainty Intervals for Cumulative COVID-19 Death Forecasts in Europe
An unintentional upload error to our data visualization tool has resulted in IHME issuing incorrect ranges of cumulative deaths in Europe related to COVID-19 in an April 6 press release and on its website.
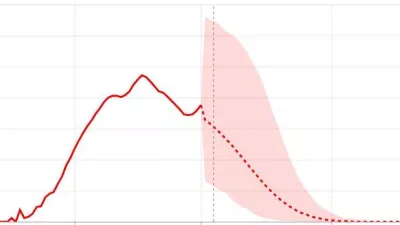
New COVID-19 forecasts for Europe: Italy & Spain have passed the peak of their epidemics; UK, early in its epidemic, faces a fast-mounting death toll
New COVID-19 estimates find that, among European nations, the peak daily death rate from the pandemic will occur during the third week of April, with the pandemic spreading from Southern Europe.
New IHME COVID-19 forecasts find lower hospital bed need, epidemics starting to peak confirms social distancing works
Updated COVID-19 estimates find that need for hospital beds, ICU beds, and ventilators needed to deal with the COVID-19 epidemic are less than previously estimated.
New COVID-19 forecasts: US hospitals could be overwhelmed in the second week of April by demand for ICU beds, and US deaths could total 81,000 by July
In a forecast based on new data analyses, researchers find demand for ventilators and beds in US hospital intensive care units (ICUs) will far exceed capacity for COVID-19 patients as early as the second week of April.
Low back and neck pain tops US health spending
Americans in 2016 spent an estimated $380 billion on low back and neck pain, as well as on joint and limb pain, and other musculoskeletal disorders.
Chronic kidney disease a ‘global killer in plain sight’
Rates of people needing dialysis have increased more than 40% since 1990, but access to this life-saving treatment is still markedly inequitable, according to a new scientific study.
Men twice as likely as women to die of liver cirrhosis
Twice as many men as women are dying from liver cirrhosis, according to a new scientific study.
Sepsis associated with 1 in 5 deaths globally, double previous estimate
Twice as many people as previously believed are dying of sepsis worldwide, according to an analysis published today in The Lancet. Among them are a disproportionately high number of children in poor areas.
Probability of dying from road injury has dropped worldwide in all but 5 nations
Road injuries have become more frequent but less fatal over the past three decades, according to a new scientific study. The probability of dying from a road accident increased in only five nations since 1990 – Central African Republic, Jamaica, Somalia, Swaziland, and United Arab Emirates.
Findings on education, malnutrition ‘deeply disturbing’ with United Nations’ goals 10 years away
For the first time, researchers have mapped years of education and child malnutrition across all low- and middle-income countries at the level of individual districts. The findings include precision maps illuminating disparities within countries and regions often obscured by national-level analyses.
‘Activist editor’ Richard Horton of The Lancet receives $100,000 Roux Prize for lifetime achievement in population health
Dr. Richard Horton, the “activist editor” of the international medical journal The Lancet, will be honored June 10 in London for his accomplishments as one of the world’s most “committed, articulate, and influential advocates for population health.” He is receiving the 2019 Roux Prize, given annually to individuals on the front lines of global health innovation in data science. Past winners include health ministers of Rwanda and Mali.