News releases
Read the latest news from IHME about published research.Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) Forecasts More Than 40,000 Deaths in Indonesia by November 1, 2020
In its first projections comparing different actions to control COVID-19 transmission, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is forecasting 41,089 people (range of 16,355 to 109,761) in Indonesia will die by November 1.
New IHME Forecasts Show More Than 200,000 US Deaths by November 1
In its first projections of COVID-19 deaths out to November 1, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is forecasting more than 200,000 deaths in the United States.
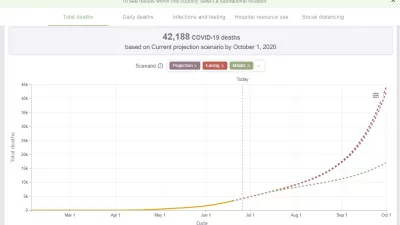
New IHME COVID-19 Forecasts Predict More than 40,000 Deaths in Pakistan by October 1
In its first projections for Pakistan, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is forecasting 42,188 people (with a range of 18,380 to 107,181) will die from COVID-19 by October 1.
Correction: New IHME COVID-19 Model Forecasts Latin American, Caribbean Nations Will See Nearly 440,000 Deaths by October 1
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is forecasting nearly 388,300 people will die from COVID-19 in Latin American and Caribbean nations by October 1.
New IHME COVID-19 Forecasts for Arab League Nations Find More than 50,000 Deaths in Egypt
In its first projections for nations of the Arab League, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is forecasting 53,366 people (with a range of 23,158 to 113,903) in Egypt will die from COVID-19 through October 1.
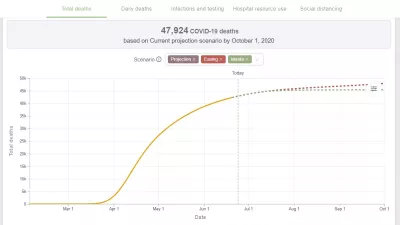
New IHME COVID-19 Forecasts UK Facing Nearly 50,000 Deaths by October 1
In its first projections comparing different actions to control COVID-19 transmission, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is forecasting 47,924 people (range of 46,131 to 50,319) in the UK will die by October 1.
New IHME COVID-19 Model Forecasts 88,160 Deaths in Mexico by October 1
In its first projections comparing different actions to control COVID-19 transmission, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is forecasting 88,160 people in Mexico will die through October 1.
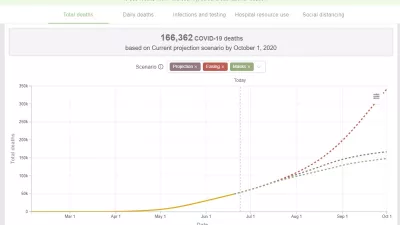
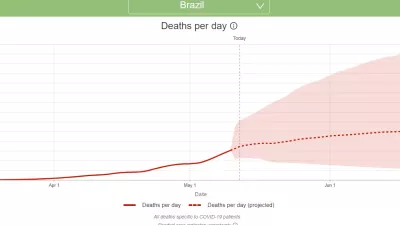
New IHME COVID-19 Model Forecasts More Than 166,000 Deaths in Brazil by October 1
In its first projections comparing different actions to control COVID-19 transmission, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is forecasting 166,362 people in Brazil will die through October 1.
New IHME COVID-19 Model Projects Nearly 180,000 US Deaths
In its first projections comparing different actions to control COVID-19 transmission, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is forecasting nearly 180,000 in the United States will die by October 1.
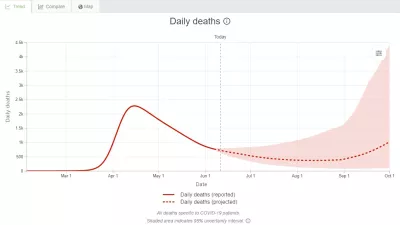
IHME models show second wave of COVID-19 beginning September 15 in US
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) has extended its US COVID-19 forecasts through October 1. The forecast shows 169,890 deaths in the US by October 1, with a possible range between 133,201 and 290,222.
New IHME COVID-19 forecasts show deaths in Mexico exceeding 50,000
New forecasts from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington find COVID-19 deaths in Mexico exceeding 50,000 through early August and beyond, a more than six-fold increase from the Institute’s previous forecast, on May 12, of nearly 7,000 deaths.
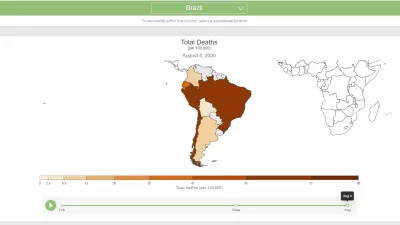
New IHME Projection Sees COVID-19 Deaths in Brazil at More than 125,000
New forecasts from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington find COVID-19 deaths exceeding 125,000 through early August and continuing to increase after that.
New Study Finds 2 Billion People Without Proper Sanitation at High Risk for Coronavirus
Without access to soap and clean water, more than 2 billion people in low- and middle-income nations – a quarter of the world’s population – have a greater likelihood of acquiring and transmitting the coronavirus than those in wealthy countries.
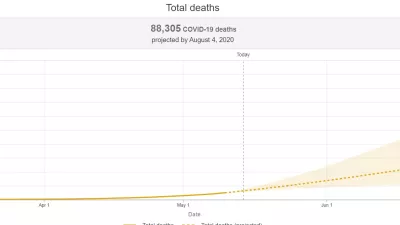
New Projection Sees COVID-19 Deaths in Brazil at Nearly 90,000
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is projecting nearly 90,000 deaths in Brazil related to COVID-19 by early August.
New IHME COVID-19 Projections: First Forecasts for Select Nations in Latin America, Asia, and the Middle East
In its first forecasts for COVID-19 deaths outside North America and Europe, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington is preliminarily projecting nearly 90,000 deaths in Brazil through early August, as well as more than 5,000 deaths each in Ecuador, Mexico, and Peru.