United States (US) health
About $4.3 trillion of the $10 trillion spent on health globally is in the US. Despite this huge investment, there are still wide disparities in health and health spending across the country.
Addressing disparities and key health issues
To understand and address the great disparities in health and health spending across the United States – a country spending more on health care than any other – IHME measures health throughout the US, using our library of health data, the world’s largest and most comprehensive, and a global collaborator network of thousands of physicians, researchers, policymakers, and analysts.
IHME identifies, investigates, and interprets the causes and effects of disease, injury, and death, and provides evidence and tools enabling stakeholders to interpret and make results relevant for their communities.
US health research areas
Global Burden of Disease (GBD)
This study measures the toll of early death and disability caused by more than 300 diseases and injuries.
- The study produces estimates of life expectancy, causes of death, and nonfatal health loss for the US as a whole and for all 50 states and the District of Columbia.
- Results are available by age group and sex for each cause of death and disability and more than 80 risk factors, from 1990 to the present.
GBD US state-level work:
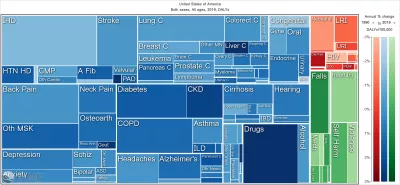

US Health Disparities
This research examines disparities in health outcomes by racial and ethnic group for every county across the United States.
Using small-area estimation methods, the research team analyzes top causes of death and poor health from 2000 to 2019 by age and sex, and for five racial and ethnic groups:
- non-Hispanic American Indian and Alaska Native
- non-Hispanic Asian and Pacific Islander
- non-Hispanic Black
- non-Hispanic White
- Hispanic or Latino
By identifying where these disparities lie at the county level, this research can play a vital role in informing efforts to address them.
Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) account for over 950,000 deaths per year in the United States, but those deaths are not distributed equally. IHME’s research on CVD levels in the US highlights disparities across age, sex, and four racial and ethnic groups: non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic other, and Hispanic. Estimates are produced for all CVD causes and relevant risk factors and are projected through 2040 using simulation models that incorporate the potential impacts of select behavioral and medical interventions.
Learn more about cVDs


Disease Expenditure (DEX)
Health loss can only be properly addressed if resources, technology, and innovation are combined with an in-depth understanding of the current health spending landscape.
- DEX research uncovers how resources are spent on US health care across health conditions, age groups, sexes, types of care, and time.
- These findings, in turn, can help health system researchers and policymakers identify the driving forces behind spending increases.
- View DEX publications
