Diet
How much disease burden can be attributed to diet, and what components of our diet are most harmful? We explore the link between dietary changes and population health.
Photo by Filip Milovac.
1.9 million
deaths globally were attributable to high-sodium diets in 2021, making it the most impactful dietary risk.
10.6%
of all deaths in 2021 were associated with poor diet, with cardiovascular disease as the leading cause of death associated with diet.
30%
of deaths from cardiovascular disease were attributed to poor diet in 2021.
Interactive data visuals
GBD Compare

Compare the impact of various dietary risks like high sodium, low whole grains, and more.
Burden of Proof
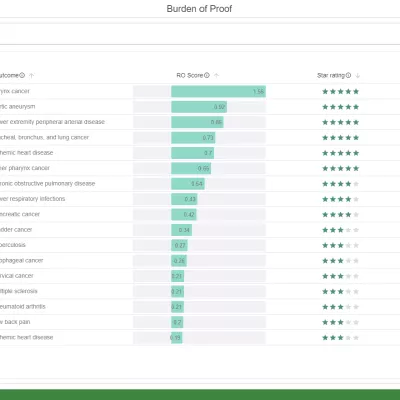
Explore the strength of evidence behind various health outcomes associated with dietary changes like eating more red meat or fewer vegetables.
Datasets in our catalog
Visit the Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx) to download our estimates and view data sources for measuring dietary risks.
GBD 2021 Dietary Risk Exposure Estimates 1990-2021
Estimate
GBD 2021 Dietary Risk Exposure Estimates 1990-2021
United States USDA Food and Nutrient Database for Dietary Studies (FNDDS)
Estimate
United States USDA Food and Nutrient Database for Dietary Studies (FNDDS)
Italy National Survey on Food Consumption 2005-2006
Survey
Italy National Survey on Food Consumption 2005-2006
Health effects associated with vegetable consumption

