Acting on Data
Discover stories from around the world about the people turning IHME evidence into health impact.We look back at a year of COVID-19
One year after we published our first COVID-19 model, we take a look back at progress made, lessons learned, and how the world has changed.
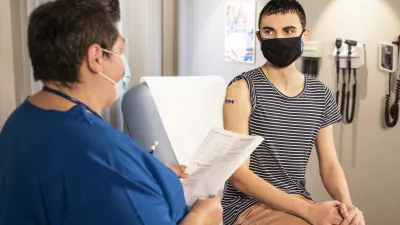
Ensuring vaccine confidence
Dr. Mokdad discusses the importance of ensuring vaccine access to any individual irrespective of their citizenship status, creating a national vaccination plan that heavily involves participation at the local level, details on the COVID-19 virus mutations, and more.
Think Global Health: Es Posible Que Nunca Lleguemos a la Inmunidad Colectiva
La vacilación ante la vacuna y otros riesgos de comportamiento reducen la probabilidad de inmunidad colectiva.
COVID-19 Maps of Vaccine Confidence
Maps of vaccine confidence globally and specifically in the United States.
COVID Projections: January 8, 2021 update
This week, IHME has decided not to release new projections due to significant delays in death reporting during and following the holidays.
20 IHME Visuals Published in 2020
20 figures from studies that our researchers and collaborators published in journals in 2020, as well as data visualizations, infographics, GIFs and designs from other IHME-affiliated projects.
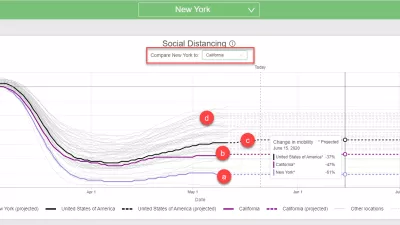
COVID-19 dataviz release notes for week of May 18
Here we summarize two new views that are available for each chart. For a more detailed walk-through, check out this video tutorial.
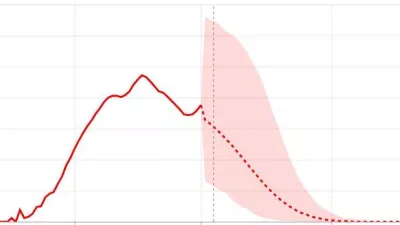
Why our COVID-19 total death projections for the United States more than doubled
With many locations at or past their initial peak in daily deaths, on May 4, we released an adaptation of our model of the initial peak in deaths that links that model to our emerging understanding of disease transmission dynamics. This new hybrid approach between our initial statistical model and a more traditional disease transmission model will enable the exploration of changes in transmission intensity if – or as the data increasingly suggest, when – social distancing mandates are eased and/or human mobility patterns rise.
Our COVID-19 forecasting model, otherwise known as “the Chris Murray Model”
The White House recently referenced a new COVID-19 forecasting model created by Dr. Christopher Murray and researchers in Washington state that predicts the state-by-state impact of the coronavirus pandemic on health systems in the United States. That model is our model.
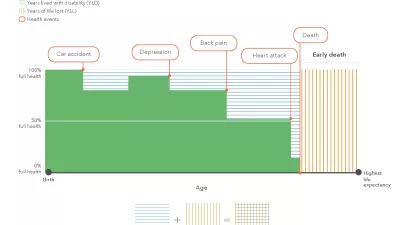
What we measure and why
Why do GBD researchers bother to use new and potentially unfamiliar metrics instead of tried-and-true, older ways of discussing disease, like prevalence and incidence? To illustrate how GBD metrics complement other population health metrics, let’s consider some standard public health metrics, and how GBD-specific metrics build on them.
Determining tobacco's cost in Arkansas
As part of a recent bipartisan push to enact new anti-tobacco legislation in the state, the Arkansas Center for Health Improvement (ACHI) used data from the Global Burden of Disease study and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) to highlight the steep cost of tobacco use in Arkansas.
UNFPA uses Global Burden of Disease metrics for project prioritization
At the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), health innovators are using Global Burden of Disease (GBD) metrics to improve child health, increase access to family planning services, and make childbirth safer.
Indonesia unveils provincial Burden of Disease study to inform national development plan
On April 4, 2019, the Indonesian Ministry of National Development Planning, known as Bappenas, and the Ministry of Health unveiled findings from a new provincial-level study of burden of disease, which they are using to guide national planning and priority setting.
UNICEF data dashboard incorporates Local Burden of Disease data
As a world leader promoting the health of children and mothers, UNICEF and its partners work to save the lives of millions of the world’s most vulnerable, in part by having hyper-local data at their fingertips. Recently, UNICEF and its partners started using maps from the Local Burden of Disease (LBD) project, an initiative led by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME), in one of their flagship data dashboards, the Equitable Impact Sensitive Tool (EQUIST).
The power of models
Every day we encounter and use mathematical models. From producing weather predictions for the week, to calculating a country’s GDP, to estimating the impact of vaccinations, models help us process, represent, and understand the data that describe the workings of the world around us.